Peer Review Process
Peer review
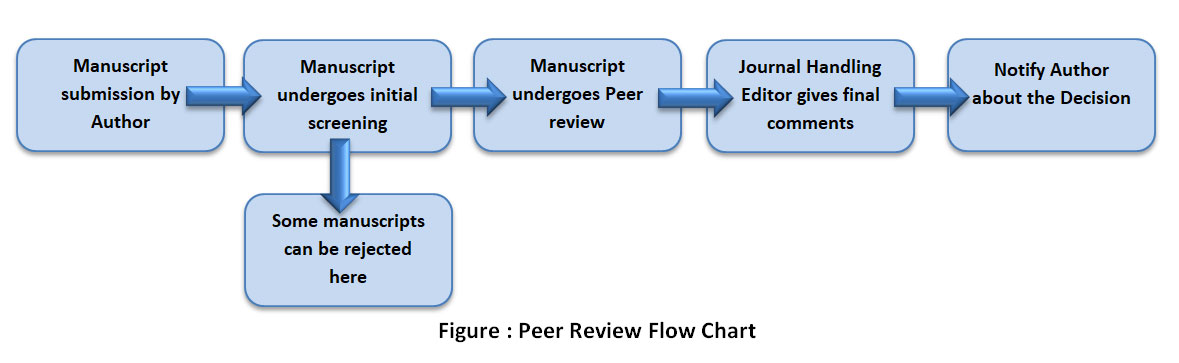
The basic idea of a peer review process is to validate the written investigative findings from a group of authors that are further assessed by a group of field experts (referees) for relevance, novelty, and accuracy. These experts usually do not belong to the editorial staff of a journal and provide their opinion unpaid. A quality peer review process makes papers more robust by pointing out gaps in findings that might need additional explanation; any misleading or unproven findings get eliminated during this process. The main goal of a peer review process is to decide if the findings of a manuscript are valid and worth publishing. This stringent publishing process that peer reviewed journals follow based on Cope Guidelines and should be one of the most important things you should consider when choosing a journal.
Our Review Key points
- MSRI reviews are rigorous, standardized, constructive, fair and efficient
- Two review phases.
- Reviewers and the handling Editor are responsible for review judgement.
- Average time for final decision: 40 days.
Peer Review Phases
The review process have three phases, the reviewers assess the manuscript independently from each other and from authors in accordance with standardized review template of our journal. The handling Editors and Chief Editor can also enter the Review Forum and oversee the review process if require.
Phase I- Post-Submission phase
On receipt of manuscript an Associate Editor of the relevant specialty section is immediately invited to take on the manuscript editorial assignment. After a preliminary content check, the Editorial assistant then assigns the manuscript out for review to the reviewers suggested by Editor.
Phase II-Review Phase
- During the Review phase, the reviewers assess the paper independently according to our standardized review report template.
- The reviewers are asked to submit the Review Report within a few weeks after accepting the assignment.
- Once all reviewers have submitted the review report, then authors are asked to respond and/or submit a revised manuscript within 15-20 days, depending on the level of revisions requested by reviewer.
- The review is complete once all review comments have been addressed to the reviewers’ satisfaction.
Phase III – Manuscript Acceptance or Editorial Rejection
Manuscript Acceptance
The final decision for the acceptance of manuscript is taken by our Handling Editors; they can then either accept the final version of the manuscript, or request further changes as necessary, typically within a few days. Acceptance of a manuscript will be done after inculcating editor’s recommendations.
The article processing fee is payable within 30 days of acceptance and is required before final publication of the manuscript.
Editorial Rejection
If the manuscript is rejected by the handling Editor, it will be considered as final decision.
The submitted manuscripts when goes through the final comments by Editor-in-Chief/Managing Editor/Associate Editor, their decision is based on the below mentioning’s:
• If manuscript is not in proper structure or any Ethical issues were identified.
• If the content of this manuscript does not meet the standards of the journal.
• If manuscript lacks the necessary detail for readers to fully understand the authors’ analysis.
• If manuscript has no new science
• If manuscript does not clearly explain which parts of the findings is new science, versus what was already known
• If manuscript doesn’t have up-to-date references or has poor language quality.
• If manuscript contains theories, concepts, or conclusions that are not fully supported by its data, arguments, and information.
• If manuscript does not provide enough details about materials and methods to allow other scientists to repeat the experiment
• If manuscript is lacking clear descriptions or explanations of: Hypotheses tested, the experimental design, sample characteristics and descriptive statistics.
• If manuscript describes poor experimental design, or faulty or insufficient statistical analysis.
• If manuscript could not be sufficiently revised by the authors to address the concerns raised by the reviewers or editor during the review process.
 Material Science Research India An International Peer Reviewed Research Journal
Material Science Research India An International Peer Reviewed Research Journal