Comparative Analysis of Characteristics of Stainless Steel Cellular Material Prepared through Powder Metallurgy Using Accicular and Crushed Urea as Spaceholder
Shailendra Joshi*
1Department of Mechanical Engineering, NPSEI, Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand, India
Corresponding Author E-mail: shailme09@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160211
Article Publishing History
Article Received on : 16-Oct-2018
Article Accepted on : 27-May-2019
Article Published : 31 May 2019
Plagiarism Check: Yes
Reviewed by: Gauri Khanolkar
Second Review by: Neha Gupta
Final Approval by: K. M. Garadkar
Article Metrics
ABSTRACT:
Stainless steel has an excellent mechanical property as well as high corrosion resistance. Stainless steel foams, therefore, seemed like an attractive material for impact energy absorption applications where damping capability is required such as in vehicles and buildings. Also when stainless steel foam is produced as stainless steel foam, the material density will be reduced thus the resulting foam will be a combination of light weight and high strength that can also be used in high strength applications. In our analysis, we tried to produce stainless steel foam through powder metallurgy in order to control mechanical properties in a better manner compared to the casting method. Also, we try to compare the pore morphology in foams on changing the space holder from accicular urea to crushed urea using FE-SEM. The properties of stainless steel foam, to a large extent, are found to depend on the arrangement of the pores which is decided by the space holder utilized during its synthesis using powder metallurgy route. The stainless steel obtained using acicular carbamide as space holder is found to possess acicular or irregular pores whereas those produced with crushed urea as space holder possesses nearly circular holes. Also, the previous foams are found to have better mechanical properties contributing towards more useful metallic foam.
KEYWORDS:
Acicular; Arrangement; Crushed; Damping; Foams
Copy the following to cite this article:
Joshi S. Comparative analysis of characteristics of stainless steel cellular material prepared through powder metallurgy using accicular and crushed urea as spaceholder. Mat. Sci. Res. India;16 (2).
|
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Joshi S. Comparative analysis of characteristics of stainless steel cellular material prepared through powder metallurgy using accicular and crushed urea as spaceholder. Mat. Sci. Res. India;16 (2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2EITvga
|
Introduction
Metal foams are cavitied structures occupied by solid metal with gas-filled pores acquiring a large volume. They have various unique properties simultaneously such as low density (greater porosity), high compression strength, higher stiffness, more energy absorption property & low thermal conductivity which make it desirable for structural & functional applications.1 The commonly used metal foams are made up of aluminium, titanium, tantalum and steel. The microstructure of metal foams consists of a complex combination of solid and void phases.2 The voids have random shape & size and most don’t follow any pattern. Therefore randomness, which is obviously introduced into metal foams during manufacturing processes, is creating more uncertainty in the behaviour of metal foams compared to solid steel. Therefore, studying the cause and control of uncertainty in the structures of metal foams is more beneficial since they will cause a variation in their properties.
Various methods exist for the manufacture of stainless steel foams such as melt-gas injection, powder metallurgy, investment casting, melt-foaming and melt infiltration.3-5 Since powder metallurgy is cost effective and flexible it has been considered a suitable method for stainless steel foam fabrication.6-7 Also, it results in better uniform distribution of pores in foams, more precise control of process variables and pore size8 & high relative density. Steel foam is a material that can create materials with a variety of different morphologies that have desirable mechanical properties. Metal foams have an extended stress plateau in their compressive stress-strain curves, which is effective for absorbing energy at a constant stress level.
Metal foams are effective in automotive, railway, aerospace and chemical applications, where low weight, reduced chemical pollution and a high degree of comfort and safety are needed.9
Experimental Work
Measurement
In order to obtain porosity 40, 50 & 60% in the resulting structure, the stainless steel -316 L powder and acicular urea are individually packed in different packets in required quantity after measurement in the electronic weighing machine. Now corresponding to 40% porosity, the contents of packets of ss and acicular urea powder are placed inside crucible for nearly 14 minutes. Repeating the same for 50 and 60% porosity packets. In a similar manner, the samples of crushed urea particles are prepared to maintain porosity 40, 50 & 60%.
Mixing and Preheating
These properly mixed powders in appropriate amounts are placed inside a cylindrical die of 10 mm diameter and are subjected to a pressure of 250 MPafor 30 seconds producing green compacts of a cylindrical shape complementary to die inner portion. After that, the green compact samples of low strength are preheated in a cylindrical furnace at 3500C, for nearly two and a half hour.
Sintering
The preheated samples are heated up to 11100C and kept at the same temperature for about 115 minutes. Heating rate maintained during sintering is 120C /min. For preventing any residual stresses and structural deformation, the samples remained in the furnace for a time period of 65 min. As a result, the volume of the samples attains a uniform temperature of 1100°C. Afterwards, these specimens are kept in the furnace for cooling.
The microstructure arrangements of both types of distinct ss foam samples obtained using acicular and crushed carbamide are viewed on a Scanning Electron Microscope.
The mechanical properties of the samples are characterized after performing a compression test on the specimen on the Instron universal testing machine at the strain rate of 10-3 s-1.
Results and Discussion
Green compact samples compacted surface are analyzed on FE-SEMThe microstructure shows the position of urea particles in the stainless steel matrix in the figure. In the image, the black area shows stainless steel particles whereas white regions represent the urea particles in the matrix. We can observe from the SEM images that larger sized pores result in case of green stainless steel compacts containing acicular urea whereas small size uniformly distributed pores in case of that containing crushed urea particles. This occurs due to variation in the size of urea particles and contributing mixing in crucible.
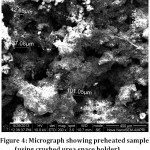
Due to the evaporation of urea particles, whether acicular or crushed, during preheating of green compact samples the pores gets produced. The pores obtained are larger in case of samples resulted from acicular urea than that of crushed urea particles due to deformation and distortions resulted by an increase in temperature and evaporation. Pores dimension are more compared to the size of urea particles since urea particles vaporise after destroying the mechanical bonds that created high dimension voids.
After preheating both types of samples are sintered to give strength and produce metallurgical bonds in the stainless steel foam samples. The preheated part is heated at a temperature greater than the preheating temperature but below the melting point of the matrix .
The samples with a higher percentage of urea are irregular in shape because after preheating of green compacts, the samples with a higher percentage of urea have higher porosity making the pre-heated compact much weaker. Due to less bonding strength, the samples having a higher percentage of urea did not sustain its shape after pre-heating. The irregularity in shape is more in case of samples obtained through acicular urea particles than that obtained from crushed ones but the strength is increased after sintering. The pores resulted beyond sintering are less in dimensions than those of the pores produced after preheating due to the large restoring force producing more pore shrinkage during sintering.
Figure 1: Microstructure showing acicular carbamide particle in the green compact
Figure 2: Microstructure of crushed carbamide particles in the green compact
Figure 3: Micrograph showing preheated sample (using acicular urea space holder)
Figure 4: Micrograph showing preheated sample (using crushed urea space holder)
Figure 5: Sintered stainless steel foam samples with varying porosity processed using acicular crystals of urea
Figure 6: Sintered Stainless steel foam samples with varying porosity processed using fine urea particles
Figure 7: SEM image showing a sintered foam sample (using acicular urea space holder)
Figure 8: SEM image showing a sintered sample (using crushed urea space holder)
The pores obtained in case of sintered foams while utilizing acicular urea as space holder are acicular whereas in samples containing crushed carbamide as space holder are nearly abut circular in shape. This is due to the shape of space holder particles and metallurgical bonding in stainless steel matrix during sintering.
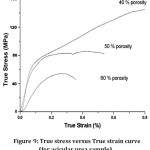
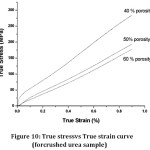
During the compression test of stainless steel foam samples of 40, 50 & 60% porosity. In case of ss foam samples comprising of acicular urea as spaceholder, the plateau region is obtained when the porosity reaches 50 vol % & beyond it whereas it is not distinct in case of samples obtained from crushed urea as spaceholder due to large size acicular pores obtained in the previous case. They have high energy absorption capacity. The foam samples yield strength lowers with the increase in porosity in a later case. Also, the material is ductile and can be used in lightweight structural applications.
Figure 9: True stress versus True strain curve (for acicular urea sample)
Figure 10: True stresses True strain curve (for crushed urea sample)
Conclusion
Thus stainless steel foams could be successfully processed through powder metallurgy and ureacan be efficiently used as a space holder. Alsothe amount of porosity and material density is directly proportional to the amount of space holder usedThe pores dimensions produced depends on the nature of space holder utilized, sintering temperature and time interval of preheating &sintering.
The foams containing larger dimensions pores showed distinct plateau regions at 50 and 60 vol. % porosity corresponding to a plateau stress of 80 and 55 MPawhereas those possesing circular pores doesn‘t possess distinct plateau regionThe processed acicular foams having distinct plateau regions shows their impact energy absorption characteristics& those processed with crushed urea as a space holder can be utilized in high strength structural applications.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks MANIT, Bhopal& CSIR-AMPRI, Bhopal for providing support during the study and research.
Funding Source
The author declares that the funding is done by author only.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- V. C. Srivastava, K. L. Sahoo, “Processing, stabilization and applications of metallic foams. Art of science”, Materials Science Poland, Vol. 25, No. 3, March 2007.
- N. Babcsán, J. Banhart, D. Leitlmeier, “Metal Foams – Manufacture And Physics Of Foaming”, International Conference, “advanced Metallic Materials” 5 − 7 November 2003.
- Porous and cellular materials for structural applications. In: Schwartz DS, Shih DS, Evans AG, Wadley HNG, editors. MRS Symp. Proc., vol. 521, 1998.
- Mechanical properties of porous and cellular materials. In: Sieradzki K, Green DJ, Gibson LJ, editors. MRS Symp. Proc., vol. 207, 1990.
- John Banhart, “Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metal foams”, Progress in Materials Science, January 2000, pp 559–632.
CrossRef
- J.Banhart, J. Baumeister, “Deformation characteristics of metal foams”, Journal of Material Science 33, 1998, pp 1431–1440.
CrossRef
- NiuWenjuan, BaiChenguang, QiuGuibao, Wang Qiang, Wen Liangying, Chen Dengfu, Dong Lingyan, “Preparation and characterization of porous titanium using the space-holder technique”, Rare Metals, Vol. 28, No. 4, Aug 2009, pp 338-342.
CrossRef
- V. Paserin, S. Marcuson, J.Shu, Cellular Metals: Manufacturing, Properties, Applications, in J. Banhart, N.Fleck, A. Mortensen(Eds.), Verlag MIT Publishing, Berlin,2003,pp.31–38.
- Andrew Kennedy (2012). Porous Metals and Metal Foams Made from Powders, Powder Metallurgy, Dr. Katsuyoshi Kondoh (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0071-3, In Tech.
CrossRef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Material Science Research India An International Peer Reviewed Research Journal
Material Science Research India An International Peer Reviewed Research Journal