Computational Methods in Material Science-Editorial
Pages : 01-02 Sami H. Mahmood*



Vishnu Ashok Adole1 , Bapu Sonu Jagdale1*
, Bapu Sonu Jagdale1* , Thansing Bhavsing Pawar2
, Thansing Bhavsing Pawar2 , Bhatu Shivaji Desale1
, Bhatu Shivaji Desale1
In the current investigation, we wish to report a combined study on the theoretical and experimental investigation of structural, molecular, and spectral properties of ethyl 4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (EDMT). The EDMT molecule is synthesized and characterized by UV-Visible, FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT, and mass spectral techniques. The density functional theory (DFT) investigation was performed by using the B3LYP level of theory at 6-311++G (d,p) basis set. Frontier molecular orbital (FMO) analysis is likewise examined. An TD-DFT method was used for the UV-Visible spectral analysis by using the B3LYP level and 6-311++G (d,p) basis set in the DMSO solvent. Experimental and theoretical UV-Visible spectra were compared in the present study. Various reactivity descriptors are discussed. Besides, Mulliken atomic charges, molecular electrostatic surface potential (MESP), and some valuable thermodynamic functions are studied.
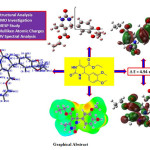 Click on image to enlarge |
Sandip S. Pathade1 , Vishnu A. Adole2
, Vishnu A. Adole2 , Bapu S. Jagdale2
, Bapu S. Jagdale2 , Thansing B. Pawar3*
, Thansing B. Pawar3*
The current examination deals with a detailed investigation on the computational study of 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole (CPMPP) by using density functional theory (DFT). CPMPP is synthesized and characterized by UV-Visible, FT-IR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectroscopic methods. The molecular structure, optimized geometrical parameters, and vibrational assignments have been established employing the DFT method, the B3LYP method, and the 6-311++G (d,p) basis set. Frontier molecular orbital (FMO) analysis and various global reactivity parameters are also discussed for the better comprehension of the chemical reactivity. Theoretical and Experimental; UV-Visible analysis is compared and a good deal of agreement is found. Experimental vibrational frequencies were compared with the theoretical IR spectrum to mark the correct vibrational assignments. Molecular electrostatic surface potential (MESP) and Mulliken atomic charges are computed at the same level of theory to locate the charge density. Absorption energies, excitation energy, oscillator strength, and transitions have been computed at TD-B3LYP/6-311++G (d,p) level of theory for B3LYP/6-311++G (d,p) optimized geometry.
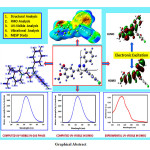 Click on image to enlarge |
Vishnu A. Adole1 , Prashant B. Koli2*
, Prashant B. Koli2* , Rahul A. Shinde1 and Rohit S. Shinde1
, Rahul A. Shinde1 and Rohit S. Shinde1
In the current examination, (E)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one has been studied to investigate geometrical entities, electronic properties, and chemical reactivity viewpoints. To inspect structural, spectroscopic, and chemical reactivity aspects, density functional theory method (DFT) at B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) basis set has been employed. The (E)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one has been synthesized and characterized by FT-IR, 1HNMR, and 13C NMR spectral techniques. The detailed investigation of bond lengths and bond angles is discussed to comprehend the geometrical framework. To explore its chemical behaviour, Mulliken atomic charges, molecular electrostatic potential surface, and electronic parameters are introduced. The imperative exploration of the electronic properties, such as HOMO and LUMO energies, was studied by the time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) method. The dipole moment of the title molecule is 2.57 Debye with C1 point group symmetry. The most electropositive carbon and hydrogen atoms in the title molecule are C14 and H27 respectively. Amongst aromatic C=C, the C16-C18 is the longest, and C17-C19 is the shortest bond. The molecular electrostatic potential plot predicts the positive electrostatic potential is around hydrogen atoms. The vibrational assignments were made by comparing the experimental FT-IR absorption peaks with the scaled frequencies obtained using computational work. Besides, some significant thermochemical information is obtained using the same basis set using frequencies.
Graphical Abstract
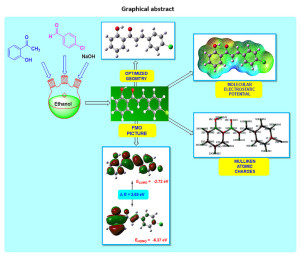 Click on image to enlarge |
Rahul Ashok Shinde1,2 , Vishnu Ashok Adole2*
, Vishnu Ashok Adole2* , Bapu Sonu Jagdale1,2
, Bapu Sonu Jagdale1,2 and Thansing Bhavsing Pawar1
and Thansing Bhavsing Pawar1
The present research deals with the synthesis, characterization and density functional theory (DFT) study of (E)-1-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (DTMPP). For the computational investigation, DFT method at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) basis set has been used. Herein, structural properties like molecular structure, bond lengths, and bond angles of the DTMPP have been explored. The all-important examination of the electronic properties; HOMO and LUMO energies were studied by the time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) method. The experimental and theoretical spectroscopic Investigation on FT-IR, 1HNMR, 13C NMR has been unveiled in the present research. To study the chemical behaviour of the DTMPP, Mulliken atomic charges, molecular electrostatic surface potential, and reactivity descriptors have been explored. The dipole moment of the DTMPP is 1.27 Debye with C1 point group symmetry and -1225.77 a.u. E(B3LYP) energy. The most electropositive carbon and hydrogen atoms in the DTMPP are C14 and H27 respectively. The C1-C6 bond is the longest (1.4089 Å) C=C bond in the DTMPP. The oxygen atom O33 is having short contact interaction with the hydrogen atom H44 with a distance of 3.3258 Å. The molecular electrostatic potential plot predicts the positive electrostatic potential is around hydrogen atoms. The FT-IR assignments were made by comparing the experimental FT-IR absorption peaks with the scaled frequencies obtained using DFT method. Furthermore, some valuable insights on thermochemical data are obtained using the harmonic frequencies at same basis set.
Graphical Abstract
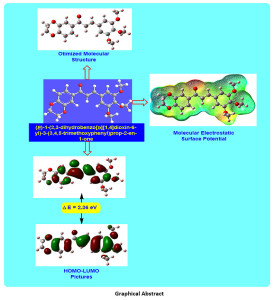 Click on image to enlarge |