Pages : 189-197
Aeysha Sultan1, Abdul Rauf Raza2, Mian Habib Ur Rehman Mehmood1, Bushra Nisar3, Syeda Laila Rubab1, Ali Irfan3 and Roberto Acevedo4*
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
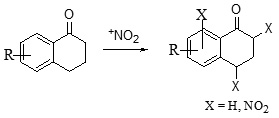
The 1-tetralone scaffold and its derivatives are not only important as pharmacological agents but these also serve as precursors for natural products and compounds of medicinal importance. The easiest way to introduce a substituent on an aromatic as well as aliphatic system is nitration. Once introduced, the –NO2 group can be easily replaced by a wide range of functional groups. The review aims to highlight strategies for nitration of substituted and unsubstituted 1-tetralone which led to introduction of NO2 functionality at various positions.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160301


PDF Downloads:
786
Pages : 198-208
C. K. Mahadevan*
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
Nucleation process is the most important stage in the formation of a crystal and has attracted the attention of researchers due to its importance in many technological and biological contexts. As the presence of impurities affects the nucleation process significantly, several studies have been made in the past to understand it. In this article is presented an overview of various studies made to understand the effect of soluble impurities on the crystal nucleation parameters of certain important materials in aqueous solution focusing the results reported by the research group of the present author.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160302


PDF Downloads:
869
Pages : 209-224
I. A. Abdel-Latif *1,2,3 and Mahrous R. Ahmed3
and Mahrous R. Ahmed3
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
Our daily need to cooling system is grown up. The used cooling systems are the source of the harmful changes in the global climate. And so, we need to search a new alternate cooling systems applying environmentally friendly technology that may help in decreasing the pollutions in our world. The progress in materials science allows to use some materials for cooling purposes. This new class of materials is so called "magnetic refrigerator". The basics of magnetic refrigeration depends on the magneto-caloric properties to reach low temperatures and obtain cooling system. The advantage of magnetic refrigerator (MR); First, the cooling efficiency is higher than conventional vapor refrigerator CVM where its cooling efficiency ~30-60% while the cooling efficiency in CVM ~ 5-10%. Second, MR can be more compactly built. Third, it is safe and an environmentally friendly cooling. In this work, we will highlight on the scientific efforts to find optimum properties to be applied as the magnetic refrigeration. In this review the highlights of the scientific efforts to seek for the best alternative materials to be used as a magnetic refrigeration applications. The low coast and small size of magnetic cooling is one the important advantage. This review consists of five sections; I. Introduction, II.Synthesis of MC materials, III. Crystal structure of MC materials and IV. Characterization and applications of MC materials, and V. Conclusions.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160303


PDF Downloads:
1010
Pages : 225-229
Banti Ganguly
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
In this short review paper we have discussed about the green nanoparticles synthesis, types, application, mechanism of synthesis and bioactivities. The green nanoparticles prove to provide clean, nontoxic materials which are important in our life survivals. This short review paper was concern with AgNPs and the reactions criterion of which such nanoparticles being prepared confined a pronounced impact on their dimension, shapes and applications.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160304


PDF Downloads:
864
Pages : 230-234
Subhasis Roy* , Argha Dey, Bhaskar Chandra Das
, Argha Dey, Bhaskar Chandra Das
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
A worldwide investigation is being carried out for improving the photoconversion efficiency of solar cells. Among all solar cells, quantum dots solar cell (QDSC) has proven as the best potential for photocurrent generator. The major focus of this research work is comparing the performance of QD based solar cells with and without the addition of synthesized dielectric nanomaterials for reducing recombination problems and higher the exciton generation. The selection of dielectric nanomaterial was carried out based on their good field-effect passivation, screened columbic attraction, enactment as a back reflector, and recombination inhibitor in solar cell. According to the above-mentioned factors lanthanum doped lead titanate Pb0.85La0.15TiO3 (PLT15) is a promising material for this research work. For improving the performance of QD based solar cells, the PLT15 paired mesoporous TiO2 electron transport layer (ETL) film was deposited onto fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) coated glass substrate using doctor blading technique followed by annealing the QD deposition onto the coated glass substrate was carried out via dipping of the glass into the QD solution for overnight. The QD used in this research work were namely – PbI3. Finally, the performance study was carried out which indicates that the introduction of dielectric material into the QDSC has proven to be as innovative and as well as efficient for improving the photocurrent conversion efficiency.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160305


PDF Downloads:
833
Pages : 235-239
Masood Ayoub* , Bilal Ahmad Bhat1, Shahjahan Ul Islam1,2, Syed Masood Ahmad Rizvi2 and Qazi Mohd Junaid3
, Bilal Ahmad Bhat1, Shahjahan Ul Islam1,2, Syed Masood Ahmad Rizvi2 and Qazi Mohd Junaid3
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
The design and development of synthetic fluorescent molecular architectures for sensing of nucleic acids and related species in living cells is an area of enormous interest. For the first time a novel compilation of single molecular abiotic fluorescent receptors for nucleic acid detection in living cells have been reviewed. Selected reports have been screened and thoroughly discussed which have revealed enormous promise for bio imaging. The mechanistic aspects of nucleic acid, phosphate or nitrogenous base sensing upon encounter with the receptors has been examined under diverse matrices. In addition to the cytotoxicity, specific conditions deciphering suitable and promising results for real-time application have been highlighted.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160306


PDF Downloads:
721
Pages : 240-251
Gulsum AYDIN1, Kenan YILDIRIM2,3 and Ayse KALEMTAS4*
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
In this study, a simple, innovative approach is applied to produce porous a-TCP-CeO2-Al2O3 composite beads via using bovine bone-derived hydroxyapatite, cerium oxide, and alumina ceramics. Bovine-bone derived hydroxyapatite was obtained via calcination of bones at 950°C for 3 hours. Hydroxyapatite is a thermally unstable biomaterial at high temperatures, and depending on its stoichiometry decomposes at 800-1200°C. Sodium alginate was successfully used as an in situ gelling templates for the production of the ceramic beads and starch, an environmentally friendly and economic pore-forming agent, is used to achieve interconnected, highly open porosity containing composite beads. Sintering of the ceramic−starch−alginate green composite beads at 1200°C for 1 hour resulted in the decomposition of the hydroxyapatite phase and formation of a-TCP. XRD analysis revealed that a-TCP-CeO2-Al2O3 composite beads were achieved. XRD analysis confirmed the formation of a-TCP phase in all composite compositions. SEM investigations of the produced composite beads revealed that bimodal pore size distribution, fine and coarse, was achieved.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160307


PDF Downloads:
762
Pages : 252-260
Buzuayehu Abebe1* , and H C Ananda Murthy1
, and H C Ananda Murthy1
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
The present work reports the synthesis of Ti-Al Oxides (TAOs) nanomaterial by an organic solvent-free impregnation method. The as-prepared products were studied by XRD, SEM-EDAX, UV-Vis, and FT-IR analytical techniques. XRD patterns revealed the fact that both TiO2 (TO)and TAOs exhibited almost similar peaks with the exception to minor peak difference in width and height which could be attributed to the alteration in the size of particles. At the calcination temperature of 500 oC, the absence of peaks for Al2O3 (AO) in the TAOs XRD pattern indicates the amorphous nature of AO. However, the appearance of Ti, Al, and O on EDAX and redshift on UV-Vis spectra confirm the successful impregnation of AO on TO. The pollutant degradation ability of TAOs photocatalyst was tested on methyl orange (MO) dye. Compared to pure TO, TAO composite has greater degradation efficiency. However, as the percentage of AO increases the degradation efficiency decreases. The conducted Langmuir model test was found to fit well for the photocatalytic reaction process following first-order reaction kinetics. Comparing the values for kinetics constant with earlier work, this work showed good MO degradation efficiency with reaction rate constant (k) values of 0.023.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160308


PDF Downloads:
705
Pages : 261-270
S.S. Mustafa
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
The performance of a flat plate solar collector with thin absorber is studied. The temperature of the absorber and its variation along the local day time is obtained by solving a heat balance equation. The temperature of the working fluid is also estimated. A published solar source functionto predict the hourly daily incident solar irradiance on horizontal surface is considered. Five absorbers of different materials: Copper, Aluminum, Stainless steel, Glass and Mica are treated. Two cooling conditions at the absorber front irradiated surface are also taken into consideration. Factors affecting its efficiency are revealed.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160309


PDF Downloads:
988
Pages : 271-279
Patit Paban Malik
View: Abstract |
PDF
| XML|
To safe environment from radioactive waste it is important to fix them as radioactive waste glasses. The corrosion behavior of radioactive waste glasses in water is significantly important. Radionuclides return to the biosphere by means of leaching from waste form into ground water. Finally the ground water containing the radionuclide are transported to the surface. In this study, the preparation, characterization and leaching behavior of some borosilicate (BS) and lead iron phosphate (LIP) of different chemical composition doped with simulated nuclear waste oxide were investigated. We measured the pH found to be in the range from 6.78 up to 7.79 of the leachate solution at normal temperature and at varying time intervals. Leaching study of these glasses were conducted with the help of Soxhlet distillation apparatus with distilled water upto 24 hours and for BS9 - BS12 upto 100 hours duration. Weight losses were are measured with respect to time of leaching. Leach rate of some borosilicate glass samples loaded with uranium are calculated from surface area measurements. The results are reported in the range 1.34x10-4 g.m-2.hr-1 and 6.26 x 10-4 g.m-2.hr-1 respectively at 90°C.
Hide Abstract
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/msri/160310


PDF Downloads:
771


 Material Science Research India An International Peer Reviewed Research Journal
Material Science Research India An International Peer Reviewed Research Journal

